Special Articles on AI Services—Document and Image Processing Technologies—
NTT DOCOMO AI-OCR for Flexible Text Recognition
Text Recognition AI OCR
Ryo Kawanami and Yusuke Fukushima
Service Innovation Department
Abstract
One technology for digitizing text appearing in a document such as an application form or receipt is OCR. While conventional OCR is limited to text recognition at fixed reading locations, recently developed AI-OCR based on deep learning supports free-form reading enabling flexible text recognition not limited to certain locations. However, when applying OCR to the Japanese language, text recognition is difficult due to a countless number of combinations of kanji (Chinese characters) and hiragana/katakana (Japanese phonetic lettering). Additionally, if support is to be provided for handwritten text, the probability of recognition errors increases. NTT DOCOMO is developing AI-OCR technology that can support Japanese in a more flexible manner with high accuracy. This article explains the mechanism of AI-OCR technology under development at NTT DOCOMO and introduces case studies of its use.
01. Introduction
-
Optical Character Recognition/Reader (OCR) reads text ...
Open
Optical Character Recognition/Reader (OCR) reads text printed on paper or another medium from within an image and enables that text to be converted to digital data. It dramatically improves accessibility to text information in real space and processing efficiency. In conventional OCR, the mainstream technique is to specify a predetermined text region and to recognize text in that region. However, with the appearance of AI-OCR that improves the flexibility of text reading using deep learning*1, text recognition that supports the reading of irregular text regions without the need for specifying any regions beforehand has become possible.
However, Japanese, a highly diverse and complex language, features a combination of different text systems called kanji, hiragana, and katakana with character shapes that are complex and diverse. In particular, kanji includes several tens of thousands of characters, so when used in combination with hiragana and katakana characters, a countless number of patterns can be formed. Moreover, unlike English, Japanese has no space between words and may be written vertically at times. Because of these features, reading and recognition in Japanese OCR processing is more difficult than that in English and other languages based on Latin characters.
Against this background, NTT DOCOMO has developed text-reading technology that provides flexible and high-accuracy support for the Japanese language based on AI-OCR. This technology is being applied to multiple case studies beyond the reading of documents.
In this article, we describe the mechanism of AI-OCR technology undertaken by NTT DOCOMO and introduce case studies of its use.
- Deep learning: A machine learning method that enhances learning ability through a multilayer neural network that imitates the neural circuits of the human brain.
-
In general, AI-OCR consists of the two processes of ...
Open

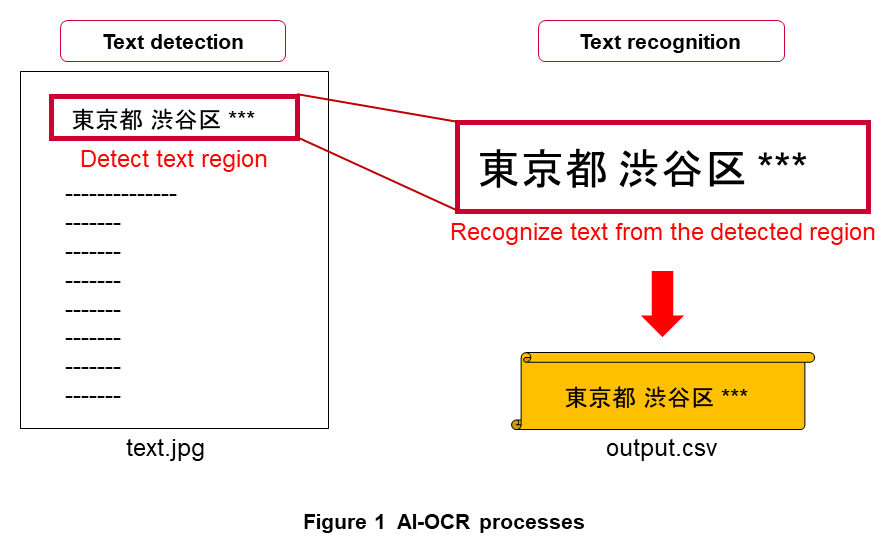
In general, AI-OCR consists of the two processes of “text detection” and “text recognition” as shown in Figure 1.
2.1 Text Detection
Text detection is the process of detecting a text region from an image containing text. In conventional OCR, a predetermined text region is specified and text recognition is performed in the next stage for that region.
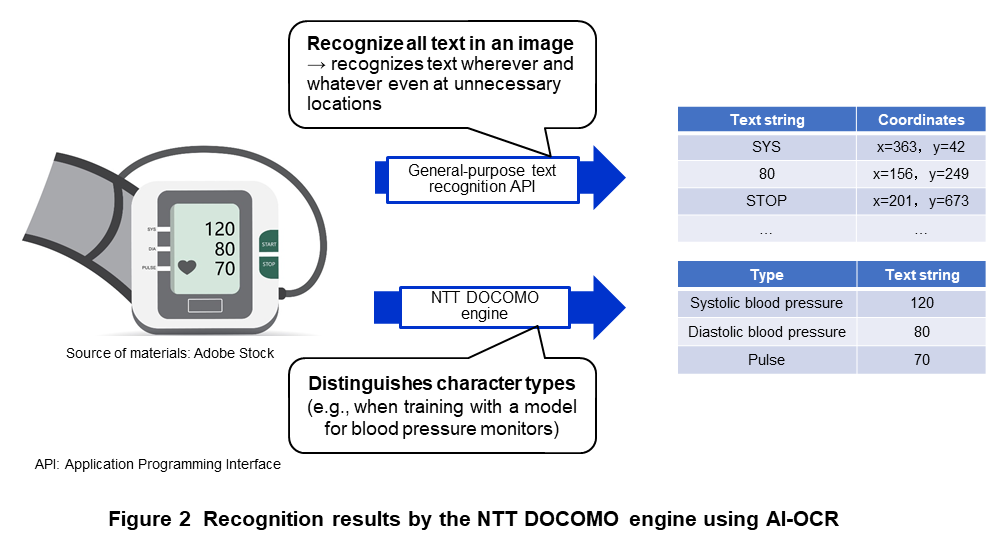
In AI-OCR, on the other hand, AI is trained with arbitrary text regions that constitute correct data as patterns. This approach enables the detection of text regions without having to specifying them beforehand. It is also possible here to learn specific text regions for which recognition is desired rather than detecting all text (Figure 2). In this way, AI-OCR can detect text regions in a flexible and versatile manner.
2.2 Text Recognition
Text recognition is a process that recognizes text within the region detected by the text detection process described above. In conventional OCR, text recognition that considers the relationship with adjacent text is difficult given that Japanese vocabulary is massive. In AI-OCR, however, training that grasps text-string patterns is possible. For example, AI-OCR can distinguish between characters that appear to be nearly the same, such as the number “0” within a numeric sequence and “O” written as an alphabetical letter.
-
3.1 Customization by Tuning Based on Original Data
Open

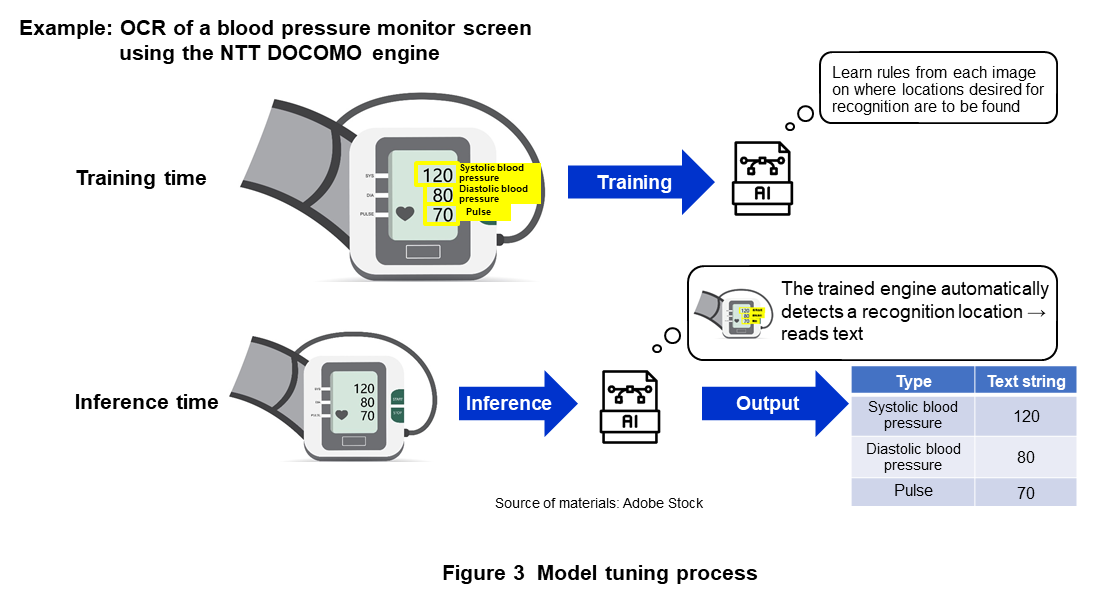
A key strength of NTT DOCOMO AI-OCR that aims for flexible text recognition is customization through model tuning. Although text can exist anywhere in real space, in most cases, the location at which the reading of text is desired is only a specific text region of interest. The reading of any other text region simply provides unnecessary information. In the past, it has been difficult to detect and recognize only a specific text region of interest from all the text appearing in an image. Fine-tuning*2 of the text-detection and text-recognition model of the AI-OCR engine developed by NTT DOCOMO makes it possible to detect and recognize only desired reading locations or desired text for application purposes (Figure 3).
In addition, the text-detection and text-recognition model is trained beforehand with original data to support Japanese language data consisting of a countless number of combinations of kanji, hiragana, and katakana. Fine-tuning based on this pre-trained model enables text recognition at an even higher level of accuracy with respect to a domain targeted for recognition.
3.2 Functional Features
The following describes three key features of AI-OCR technology being developed by NTT DOCOMO.
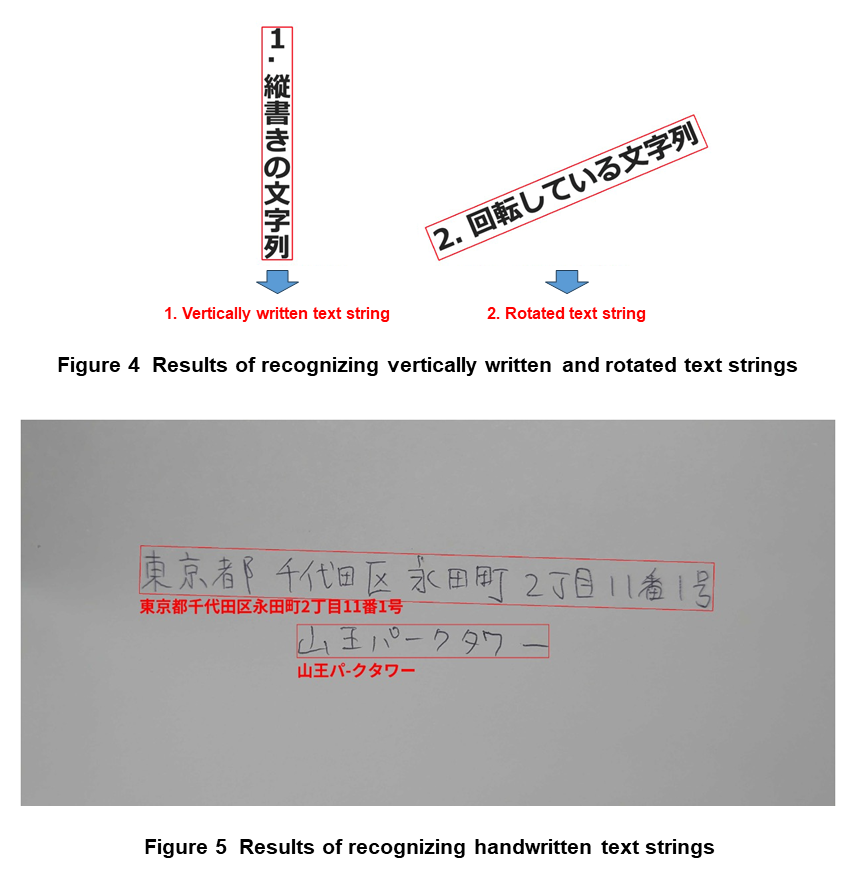
1) Support for Vertically Written Text
NTT DOCOMO AI-OCR technology supports vertical writing peculiar to Japanese as shown at the left of Figure 4. Usage scenarios for this feature include the recognition of text on the spines of books placed on a bookshelf and on signboards installed along a road.
2) Support for Rotated Text
This technology also supports the detection of rotated text as shown at the right of Fig. 4. It is rare that text photographed in real space are horizontal. To enable recognition of text in various orientations in a space, NTT DOCOMO AI-OCR technology can be applied to all sorts of scenarios regardless of text orientation.
3) Support for Handwritten Text
Finally, NTT DOCOMO AI-OCR technology features robust recognition of handwritten text as shown in Figure 5. To enable recognition to be applied to even handwritten business forms or the like, this technology adopts a high-accuracy text recognition model trained with an original dataset that includes handwritten text data. In this way, the technology achieves robust AI-OCR for both printed and handwritten text.
All in all, the above features enable text recognition in environments not limited to documents.
- Fine-tuning: The process of taking a model pre-trained using a certain dataset and retraining part or all of that model using another dataset to finely tune the parameters of the machine learning model for a new task.
-
We here introduce case studies of the use of NTT DOCOMO AI-OCR ...
Open

We here introduce case studies of the use of NTT DOCOMO AI-OCR technology. NTT DOCOMO has so far introduced its AI-OCR engine in a wide range of areas making full use of customization as described above. There are various examples of using this technology for text recognition including its embedding in the DOCOMO Image Recognition Platform [1], but here we introduce two case studies.
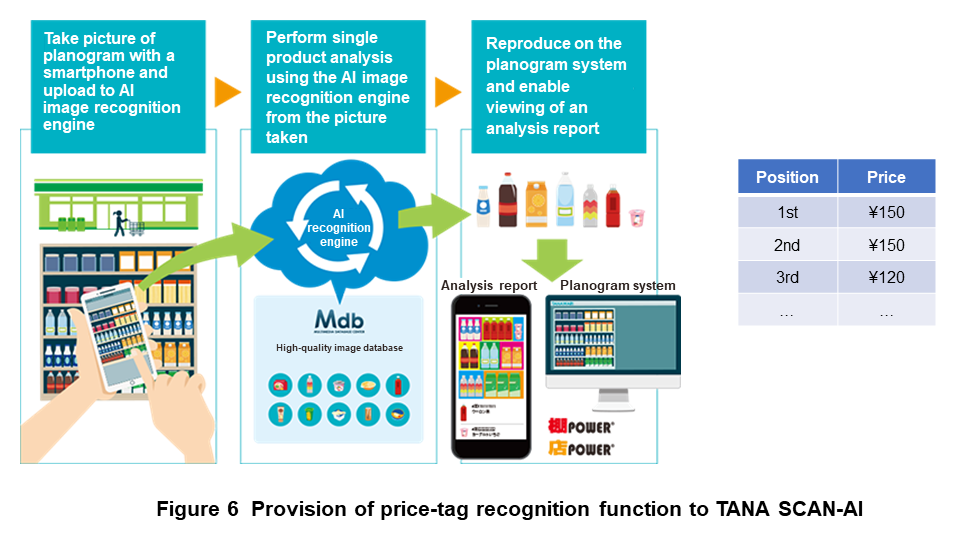
4.1 Price Tag Recognition
The following introduces the combination of NTT DOCOMO AI-OCR technology with TANA SCAN-AI [2] as an example of using this technology in the text recognition of price tags. Using NTT DOCOMO AI-OCR technology and the product image database of CYBERLINKS CO., LTD., TANA SCAN-AI is a service that judges product placement from a picture of sales shelves taken with a smartphone or other device and converts the planogram*3 into data for linking with in-store-analysis and planogram systems [2]. Applying AI-OCR technology to TANA SCAN-AI in this way enables, for example, the price of each product to be read from the picture taken of a vending machine making it easy to perform data analysis on that pricing information (Figure 6).
4.2 Bib Number Reading
NTT DOCOMO AI-OCR technology is also being applied to the reading of bib numbers used in sports events like marathons. In the EMii PicLab—Enterprise Plan— [3], a photo sales system provided by MACHIEMI CORPORATION, NTT DOCOMO’s image recognition engine provides a function for identifying contestants and a function for rejecting photos not targeted for sales due to blurring or out-of-focus problems. The AI-OCR engine is used here for the contestant identification function. Specifically, it automatically recognizes bib numbers appearing within photos and identifies the contestants tied to those bib numbers. This contestant-identification processing is performed for all photos taken at a competition thereby providing a mechanism that enables photos of each of the contestants concerned to be put on sale at a later time (Figure 7). In this way, NTT DOCOMO AI-OCR technology reduces the human operations involved in identifying contestants by manually viewing photos as done up to now.
- Planogram: Refers to the layout of how products are displayed on retail shelving.
-
This article described the functional features of ...
Open

This article described the functional features of flexible AI-OCR technology undertaken by NTT DOCOMO and its customizability by tuning to support the highly diverse and complex Japanese language. It also introduced case studies of using this technology in price-tag recognition and bib-number reading. These case studies, which are not limited to document recognition as targeted by conventional OCR, demonstrate that NTT DOCOMO’s flexible AI-OCR technology can be applied to a variety of fields. In the digital society to come, we can expect the use of OCR in even more scenarios, so it is our desire to develop functions in response to needs and to raise the value provided by AI-OCR services.
-
REFERENCES
Open

- [1] NTT DOCOMO: “DOCOMO Image Recognition Platform” (in Japanese).
 https://www.ntt.com/business/services/dirp.html
https://www.ntt.com/business/services/dirp.html - [2] CYBERLINKS CO., LTD.: “TANA SCAN-AI” (in Japanese).
 https://www.ntt.com/business/services/tanascan_ai.html
https://www.ntt.com/business/services/tanascan_ai.html - [3] MACHIEMI CORPORATION: “EMii PicLab—Enterprise Plan—” (in Japanese).
 https://www.ntt.com/business/services/emii.html
https://www.ntt.com/business/services/emii.html
- [1] NTT DOCOMO: “DOCOMO Image Recognition Platform” (in Japanese).