Organization and activities of 3GPP
Organizational structure
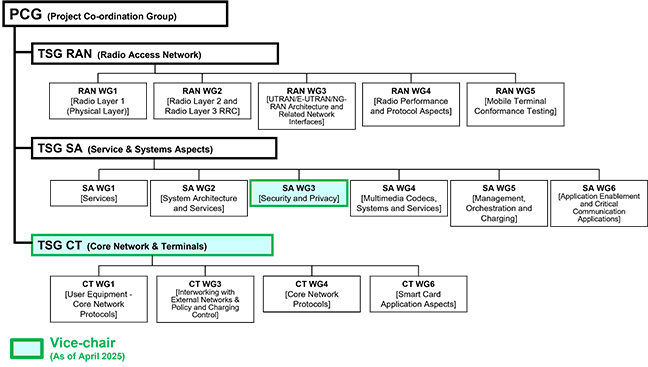
3GPP consists of a PCG (Project Co-ordination Group) and three study groups (TSG: Technical Specification Group) below it (Fig. 1).
PCG examines the overall policy of operation of 3GPP and coordinates between the TSGs (Table 1) which carry out technical examinations. Further, below the TSGs, there are multiple WGs (Working Groups) that examine the corresponding technologies.
 Click to zoom
Click to zoom
 Click to zoom
Click to zoom
Table 1 Study groups in 3GPP
 Click to zoom
Click to zoom
 Click to zoom
Click to zoom
Fig. 1 Organizational structure of 3GPP and chair and vice-chair positions served by DOCOMO
DOCOMO serves as the vice-chair in the major group in the 3GPP standardization (Fig. 1).
The roles of the chair and the vice chairs of a group are to decide policies and schedule for the standardization meetings, make decisions on agreed items and make sure to progress the discussion within the group smoothly.
Procedure of standardization
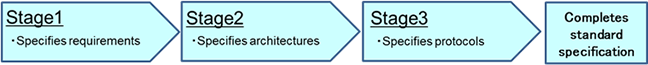
The procedure of standardization is common to TSG RAN/SA/CT, and it consists of three stages.
 Click to zoom
Click to zoom
 Click to zoom
Click to zoom
Fig. 2 Procedure of standardization
First, requirements are specified (Stage 1), then architectures are specified based on the requirements (Stage 2), and finally protocol specifications are specified (Stage 3). In each stage, a large number of mobile operators and vendors attend the meeting. Through the intensive discussions on challenges and their resolutions, standard specifications are finally completed.
Standard specifications established in 3GPP
The following table describes main standard specifications established by 3GPP, their time of completion, service names at DOCOMO and time to start the services.
| Technology | Time of completion in 3GPP | Service names at DOCOMO | Time to start the service at DOCOMO |
|---|---|---|---|
| W-CDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiple Access) |
March 2001 | FOMA | October 2001 |
| HSPA (High Speed Packet Access) |
September 2002 (Higher downlink data rates) September 2005 (Higher uplink data rates) |
FOMA High Speed | August 2006 (Higher downlink data rates) June 2009 (Higher uplink data rates) |
| LTE (Long Term Evolution) |
March 2009 | Xi,LTE | December 2010 |
| VoLTE (Voice over LTE) |
March 2009 | VoLTE | June 2014 |
| LTE-Advanced | June 2011 | PREMIUM 4G | March 2015
|
| EVS (Enhanced Voice Services) |
March 2015 | VoLTE(HD+) | May 2016 |
| IoT (Internet of Things) |
March 2016 | LTE-M, NB-IoT | October 2018 (LTE-M) April 2019 (NB-IoT) |
| 5G (5th Generation) |
June 2018 | 5G | March 2020 |